What you need to know about E. coli
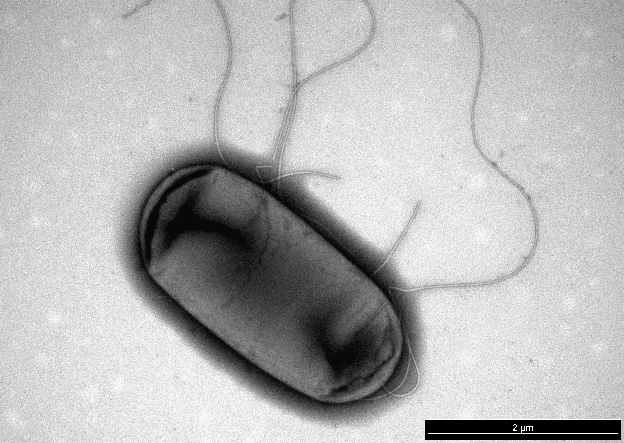
Transmission electron micrographs of E. coli, one of the kinds of bacteria that can be made resistant to antibiotics by a superbug gene known as MCR-1.
A new drug-resistant superbug gene has been discovered in meat sold in Ontario.
The gene – known as MCR-1 – makes bacteria invincible to colistin, an antibiotic used only when all other drugs have failed.
A likely source of the superbug is the agricultural industry, which in 2015 used nearly 12,000 tonnes of the drug around the world.
The number is expected to rise to 16,500 tonnes by 2021.
McMaster microbiologist Gerry Wright, director of the Michael G. DeGroote Institute for Infectious Disease Research, called that number “insane.”
“Any antibiotic class used for humans should never be used for animals (unless they’re sick,” he told the Toronto Star. “I just find it absolutely mind-boggling that we’re going into 2016 and we’re still having this discussion.”
One of the types of bacteria MCR-1 can grant resistance to is E. coli, a large and diverse group of bacteria found in the intestines of humans and animals.
Learn about the bacteria below: